Insights into Twitter Recommendation System
Published:
In this article, I will go into insights about the recommendation systems at Twitter, particularly the components that power tweet and account recommendations.
Background: I was an MLE at Twitter from 2021-2023, working on tweet and account Candidate Generation for the Home Timeline, Email and Push Notification. Below is my short write-up of the Recommendation work inside Twitter that I could remember. Most of the content and code are open-sourced. I organized them according to the components and services that I worked on during my time there.
1. Overview
Twitter tweet recommendation algorithm is the main engine behind the ranked timeline on Twitter home page. There are many components that power the computation of a ranked timeline.
But first, some numbers for scale between Twitter and TikTok:
| TikTok | ||
|---|---|---|
| New content size: DAUs (as of 2022.10): Candidates: | 500M new tweets/day ~238M Latest tweets from the last 1 day | 100M new videos/day >1B No limit on video age |
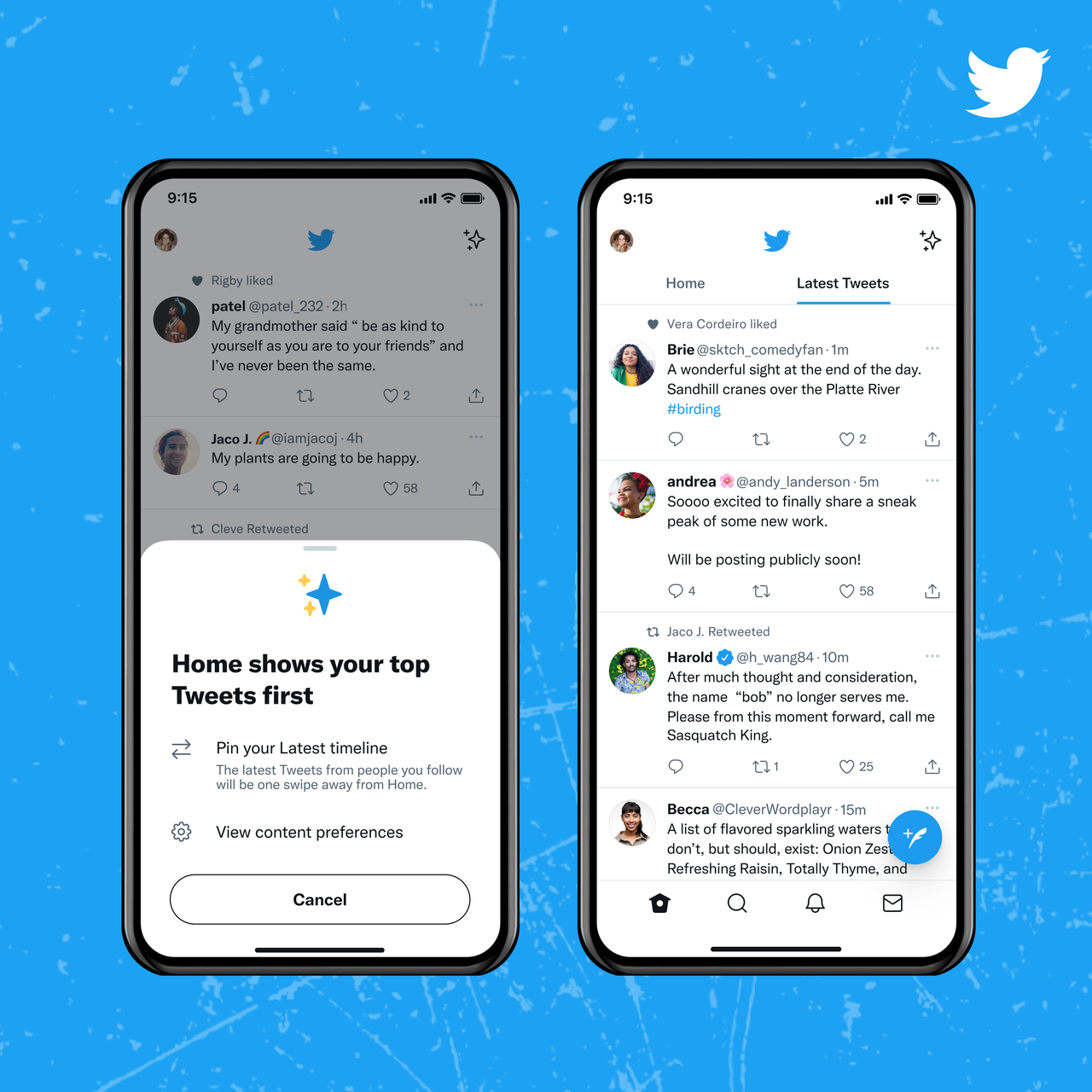
Here is the overall recommendation pipeline and its components:
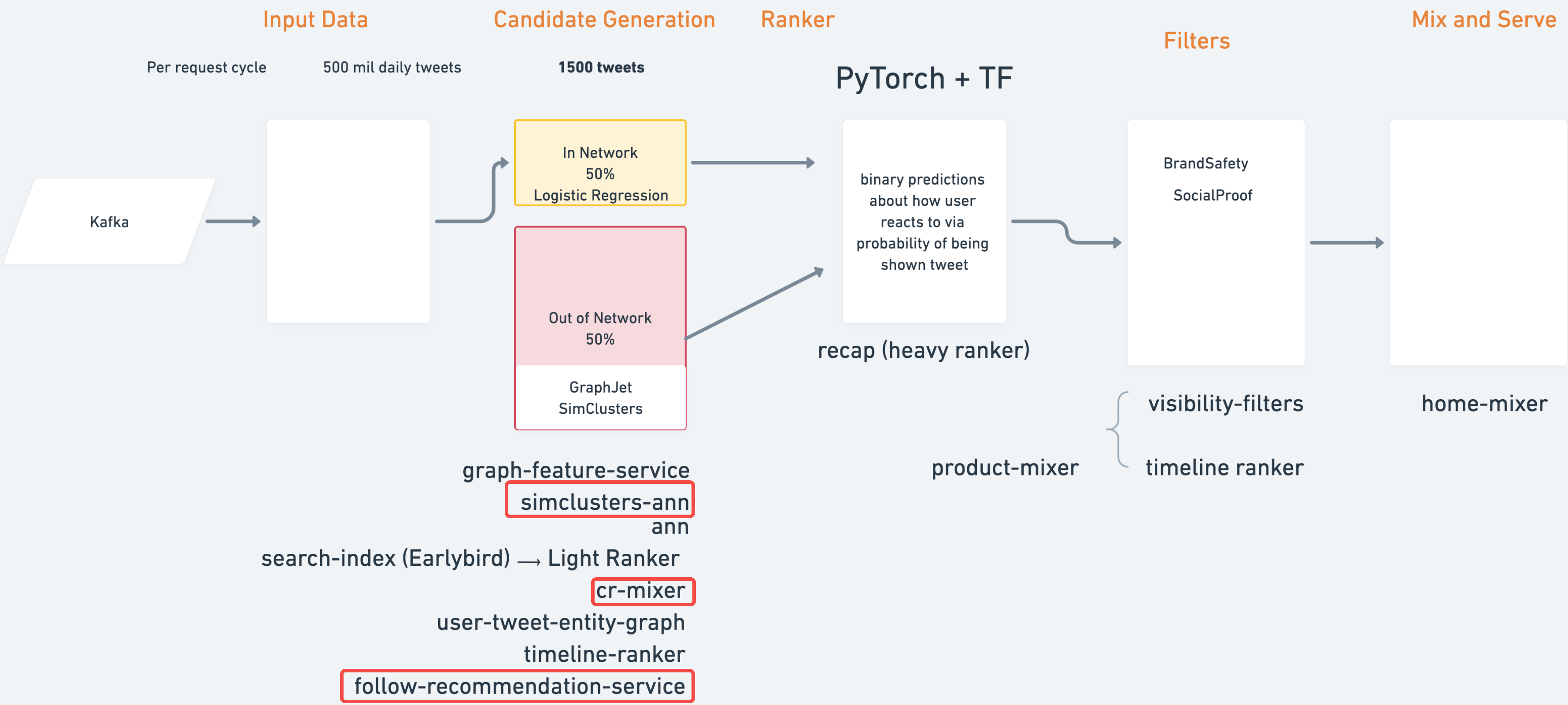
2. Candidate Generation for tweets
2.1 In-network candidate sources
In-network candidate sources is the largest candidate source and aims to deliver the most relevant, recent Tweets from users you follow. It efficiently ranks Tweets of those you follow based on their relevance using a logistic regression model. The top Tweets are then sent to the next stage.
2.1.1 RealGraph
(code)
What it is: It is a logistic regression model that predicts the likelihood of engagement between two users. The higher the real graph score between you and the author, the more of their tweets we’ll include.
Stacks: Scala Scio, Big Query ML, BQE
Algorithm: XGBoost
How it is used: Real Graph score is used as a feature in almost every downstream recommendation jobs. The downstream jobs include general candidate generation, as well as product surface recommendation jobs such as push notifications, emails and timeline. The difficulty of this job is the huge space of users (10^9) and scoring for ~N^2 pairs of users. To fix the massive scale, only recent interactions (likes, follows, profile clicks) are scored.
Real Graph delivered a huge boost for push notification DAU and MAU (minute active usage). For users that have no explicit activity (eg dormant or new users), the candidates are backfilled using the top k tweeting accounts that the given user follows. We are now able to send notifications/emails to dormant users, or even to make sure they have something ready if and when the dormant user returns.
2.2 Out-of-network candidate sources
1. Social Graph - GraphJet
What it is: realtime graph processing library that provides realtime content recommendations. GraphJet maintains a realtime bipartite interaction graph that keeps track of user-tweet interactions over the most recent hours.
Stacks: Java and Kafka.
Algorithm: GraphJet construct graph database and implements random walk algorithm (SALSA - Stochastic Approach for Link-Structure Analysis).
How it is used: GraphJet is used to request tweet recommendation given a particular user.
2. Embedding - SimClusters
What it is: An embedding algorithm that generates a sparse embedding for both tweet and author based on their engagements. The input is user or tweet, and SimClusters will return a set of similar users or tweets based on approximate cosine similarity.
Stacks: Scala Scalding batch jobs
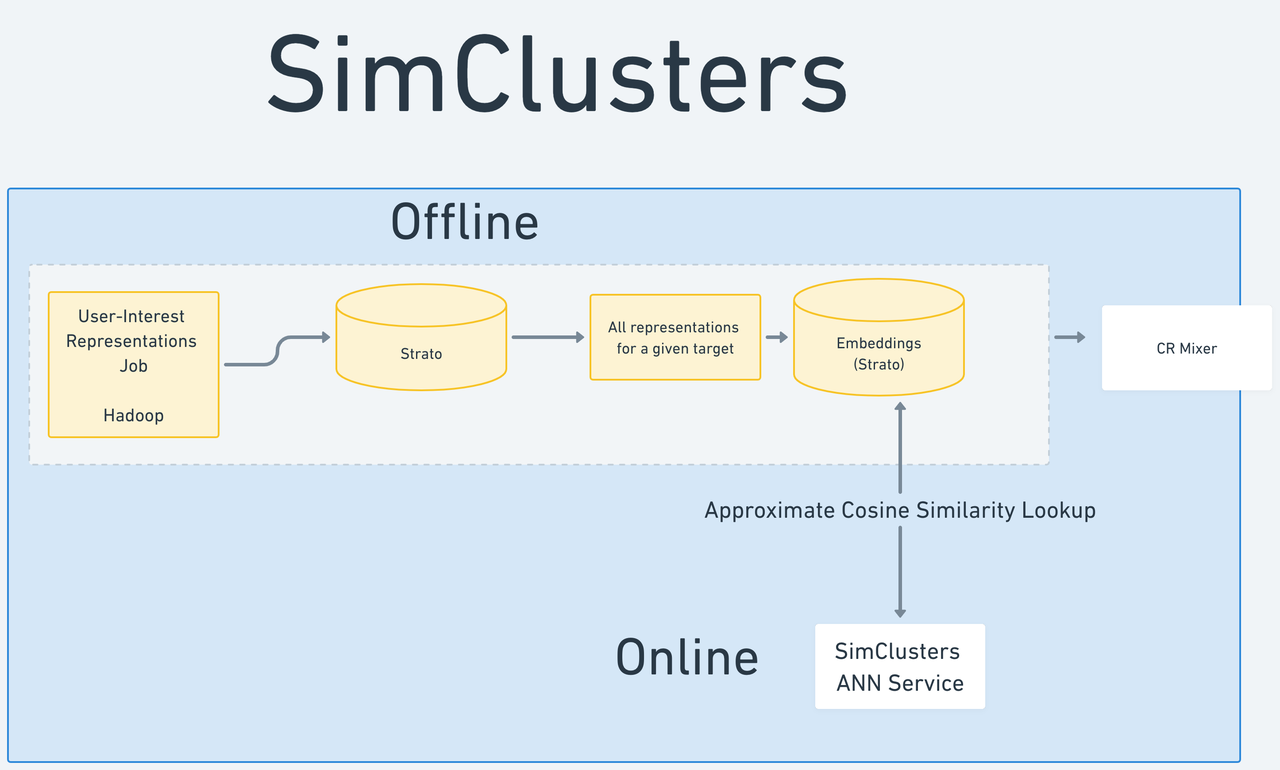
Algorithm: Construct a user-user cluster graph based on predefined community clusters (e.g. Machine learning, K-pop, soccer). Each cluster centrals are “influencers” of that topic. To construct community, use Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for community detection. The batch jobs are run every hour for tweets and every day for users.
How it is used: SimClusters are a better version of GraphJet as it works for non-homogenous data (handles both tweet and user representation at the same time). It is widely used in downstream CG for tweet and user recommendations, as well as other candidate generation algorithm as embeddings.
3. TwHIN
What it is: TwHIN (Twitter Heterogeneous Information Network) is a graph network where the nodes/vertices of the graph represent multiple entity types, and the edges represent one of many interaction types between the entities.
The following are the entities and relation TwHIN has:
Entity Types (Nodes): User, Tweet, Advertiser, Ad
Relation Types (Edges): Follow, Authors, Favourites, Replies, Retweets, Promotes, Clicks
Stacks: Pytorch Torchrec (model training), Scala Scio (hourly tweet embedding jobs)
Algorithm: We have two main TwHIN networks, each centered around high coverage relations: TwHIN-Follow and TwHIN-Engagement. Follow is a User-User graph and engagement is a User-Tweet graph. TwHIN follow and engagement graph are available on Huggingface (heavily subsampled and masked).
How it is used: TwHIN was first introduced in Twitter around 2021/2022 and received huge boost in the engagement metrics and coverage. This is due to the novelty of it being the first dense embedding at Twitter. TwHIN embeddings were quickly used in candidate generation, light ranking, and heavy ranking.
2.3 Other considerations
Here I list down a few considerations and issues arising from the Twitter recommendation system stack. Some of them are my own observations, others were something that are known internally and were being worked on.
Timeliness: Most candidate generations are produced by batch jobs and stored in a KV store, keyed by user ID. These jobs run at most every 1 hour. Therefore, most tweets are not fresh. Adding to that, some jobs are delayed by missing data.
Exceptions for timeliness: in-network tweets, Search. These are retrieved in real-time
Long tail: Because of the limitation of infra, most of the tweets need at least 8 favs to be shown as out-of-network. Low engagement tweets may never get discovered.
Popularity bias: Since most of CG algorithms are based on follow and engagement graph, authors who have a lot of followers will have their tweets shown to more people. This is a downside of “old” social media style that depends heavily on social graph.
Tweet age: Due to infra limitation on the number of tweets retrieved from these graphs, we can only get tweets within the last 1 day. For inactive or dormant users, they miss out on a lot of good content that were produced in the past.
User hierarchy: Most of twitter algorithm treats user as one of two types: consumers (users who mostly consume and don’t tweet) or producers (authors / influencers who tweet a lot). The algorithm works on serving tweets from producers to consumers. This makes it hard for normal users to reach their audience or feel encouraged to create content.
Lack of implicit signals: Most of the algorithms rely on explicit signals (likes, retweets, replies, shares). If the user doesn’t do any of those and simply consumes, it’s hard to get a good feedback. This is unlike Tiktok videos where video watch time is a very strong implicit signals. The only implicit signal we have is tweet dwell time, which is when you click into the conversation of this Tweet and stay there for at least 2 minutes.
3. Light Ranker
(code)
What it is: The light ranker is a model which predicts the likelihood that the user will engage with a tweet. It is intended to be a simplified version of the heavy ranker which can run on a greater amount of tweets.
Stacks: Python Deepbird (internal version of scikitlearn)
Algorithm: Light Ranker is a simple logistic regression. There are 2 separate models for ranking in-network and out-network tweets, with different features. The models are trained several years ago.
How it is used: Light Ranker aggregates all the candidate sources and ranks them with the likelihood that the user will most likely engage on. Light ranker returns around 400 candidates.
Issues with Light Ranker:
outdated model that are trained many years ago.
We have a newer tensorflow model in 2022, but according to the code, they seem to have reverted it back to the old version.
Our experiments on candidate source improvements were dependent on the light ranker. Some of our new candidates are rejected at the light ranker step, and so it’s hard to make significant improvement.
4. Heavy Ranker
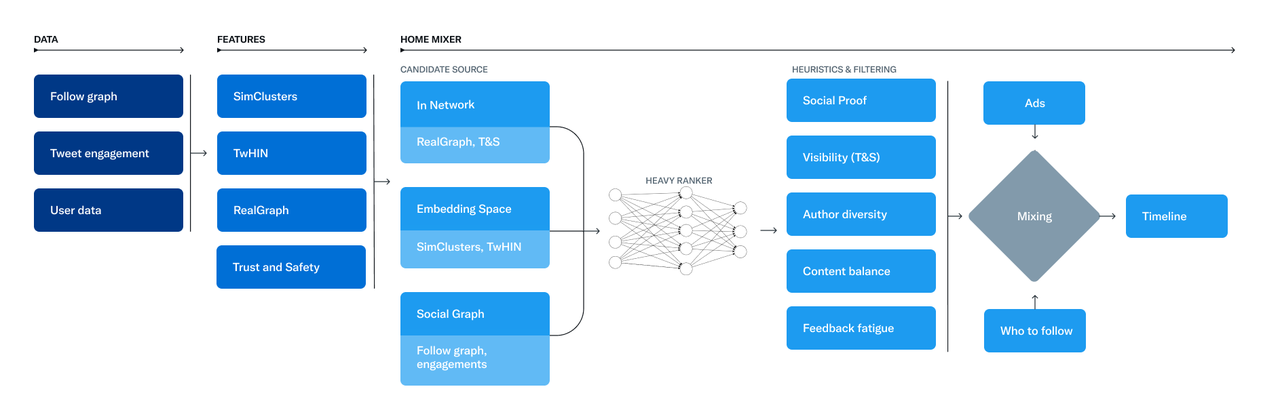
What it is: Heavy Ranker is the final stage of ranking before returning the results to the Home Timeline. It uses the candidates returned by the Light Ranker, as well as features from different sources to score them. Heavy ranker model is a real-time inference model
Stacks: Pytorch for model training and Scala for backend
Algorithm: Masknet Feature-Wise Multiplication to CTR Ranking Models by Instance-Guided Mask
How it is used: It’s important to note that there are no content-based embeddings inside the main ranking algorithm. All the features are based on engagement signals, such as “aggregate counts of user interaction with other engagers of tweets that the user interacts with”, and based heavily on “likes” and “replies” as input actions, but at an aggregate level. The social and embeddings-based features in the dataset are not used and weighted as much.
Scoring plan: After the model predicts the probability of the actions, weights are assigned to the probability. The tweet with the highest score is likely to appear at the top of your feed.
These are the actions predicted, and their corresponding weights
| feature | weight |
|---|---|
| probability the user will favorite the Tweet | -0.5 |
| probability the user will click into the conversation of this tweet and reply or like a Tweet | (11*) |
| probability the user will click into the conversation of this Tweet and stay there for at least 2 minutes | (11*) |
| probability the user will react negatively (requesting “show less often” on the Tweet or author, block or mute the Tweet author) | (-74) |
| probability the user opens the Tweet author profile and Likes or replies to a Tweet | -12 |
| probability the user replies to the Tweet | -27 |
| probability the user replies to the Tweet and this reply is engaged by the Tweet author | -75 |
| probability the user will click Report Tweet | (-369) |
| probability the user will ReTweet the Tweet | -1 |
| probability (for a video Tweet) that the user will watch at least half of the video | -0.005 |
After scoring the tweets, boost and filtering will happen:
Blue verified accounts have a multiplier of 2 or 4, which overrides many of the weights in the scoring plan.
Filtering based on your preference (remove accounts you block or keywords you mute). It also includes Trust and Safety filtering. Code
5. Difference between Twitter and Tiktok recommendation
| Tiktok | |
|---|---|
| - Mainly rely on explicit signals (likes, shares, comments) | - Use implicit signals besides explicit signals (video watch time) |
| - Recall: – Sparse embeddings – Social graph based – Only taking tweets from the last 1 day – Candidates are run in batch (for out-of-network tweets) | - Recall: – Dense embeddings – Model-based retrieval – No time limit to content – Candidates are generated in real time |